Learn More About The Cybereason Defense Platform
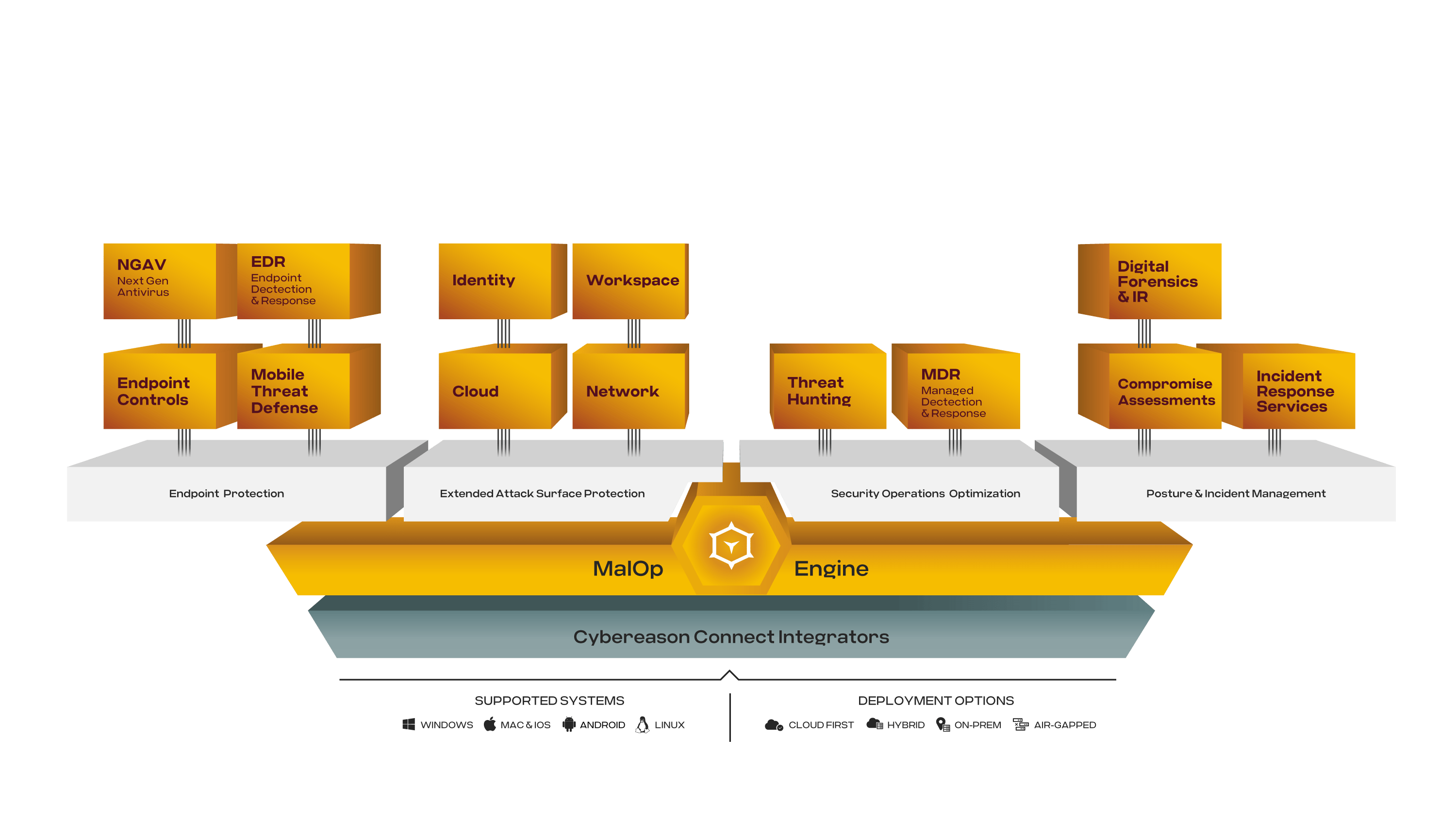
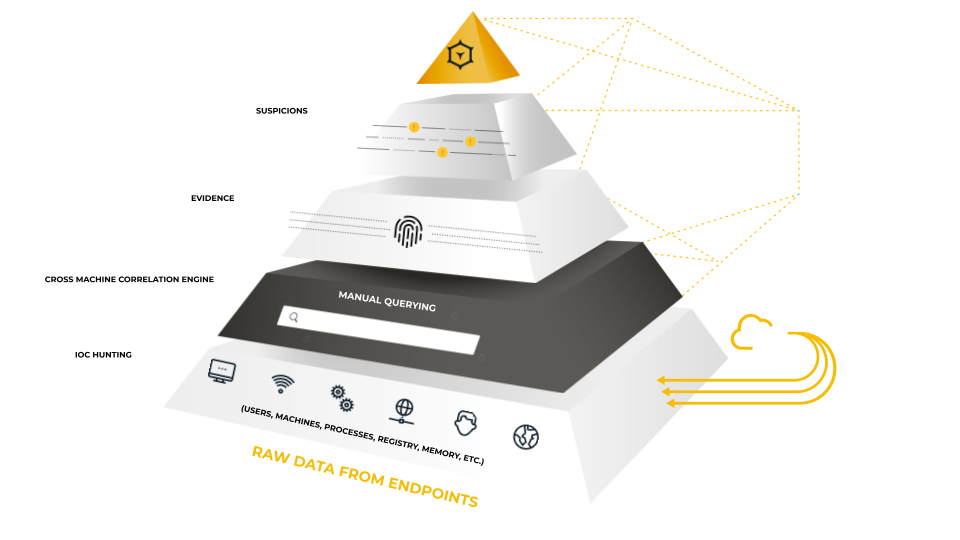
Using one agent, one console, and one team to defend all endpoints, the AI-driven Cybereason Defense Platform was designed to expose and intercept every MalOp (malicious operation).
Read the Data Sheet