For many Security Operations Centers (SOCs), conducting effective queries using a traditional Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) requires training and familiarity with syntax language, and deep analysis to take action on the results of a particular hunt.
At an enterprise scale, searches can take several minutes or longer to complete, making it cumbersome to derive new insights or successfully connect threat intelligence and investigate matches. Threat intelligence is often only matched against newly ingested data, creating coverage gaps and missed threats.
Cybereason XDR leverages a new security paradigm that uses artificial intelligence (AI) to correlate the behaviors that take place across the many ways we work: on endpoints, across identities, and on public and private networks, including protecting IoT devices and cloud infrastructure.
Let’s take a look at how an AI-driven XDR solution enables comprehensive monitoring across the entire attack surface to identify patterns and detect potential threats on a broader scale—connecting the dots between seemingly disparate or innocuous events to power 10X improvements in threat hunting.
Cybereason XDR makes building threat hunting queries orders of magnitude faster and simpler than competing solutions. Where other vendors rely on complex query languages, offer little to no visualization to support an investigation, require analysts to jump in and out of different panels, and then wait for the queries to run, Cybereason XDR enables analysts and threat hunters to operate at the speed of thought.
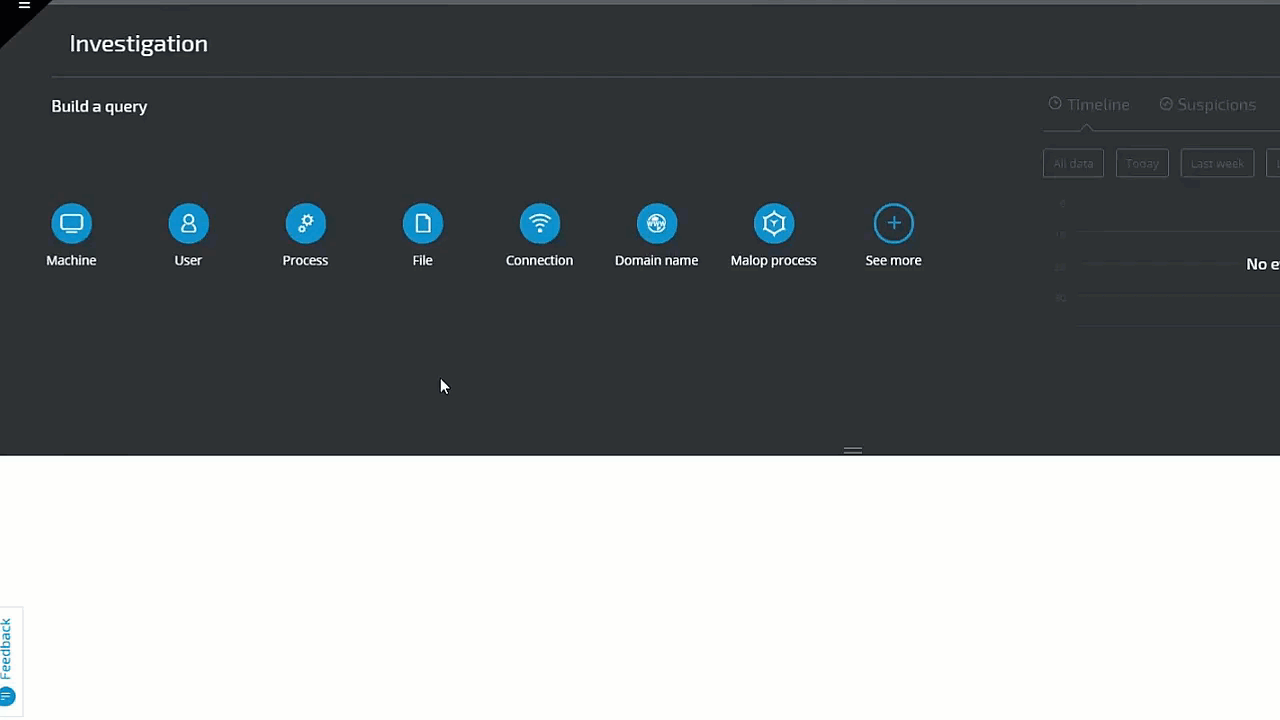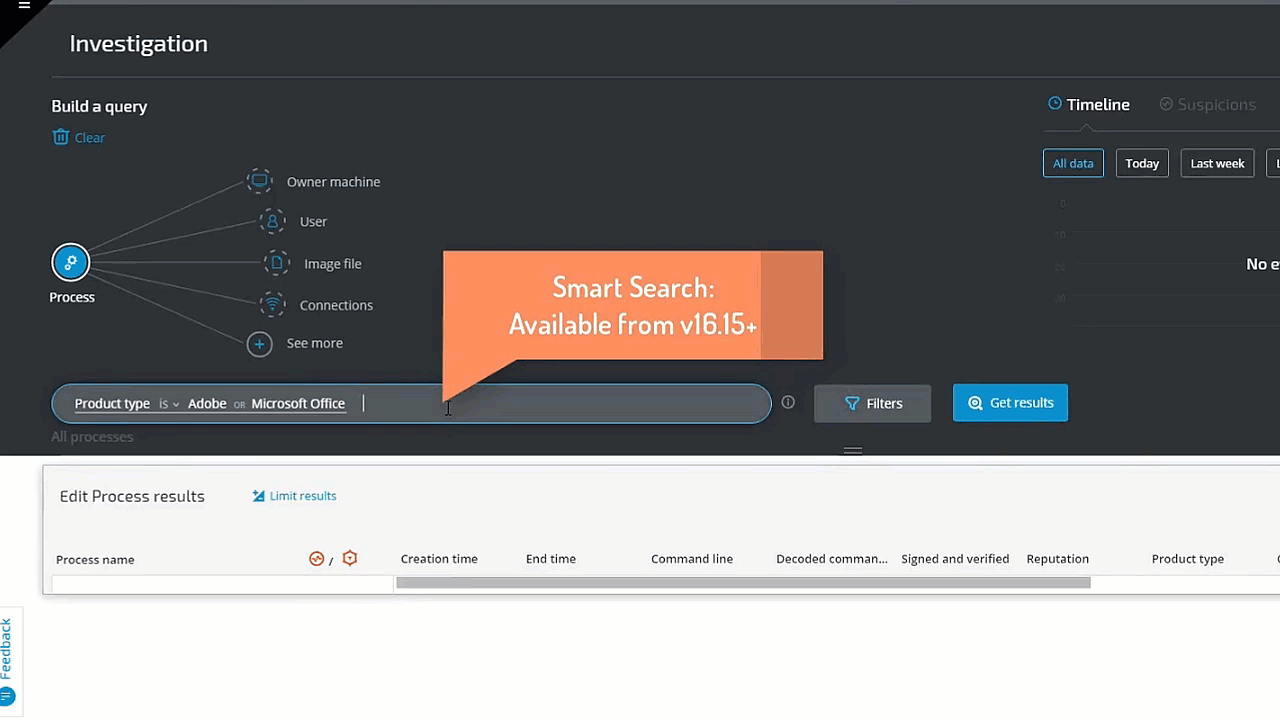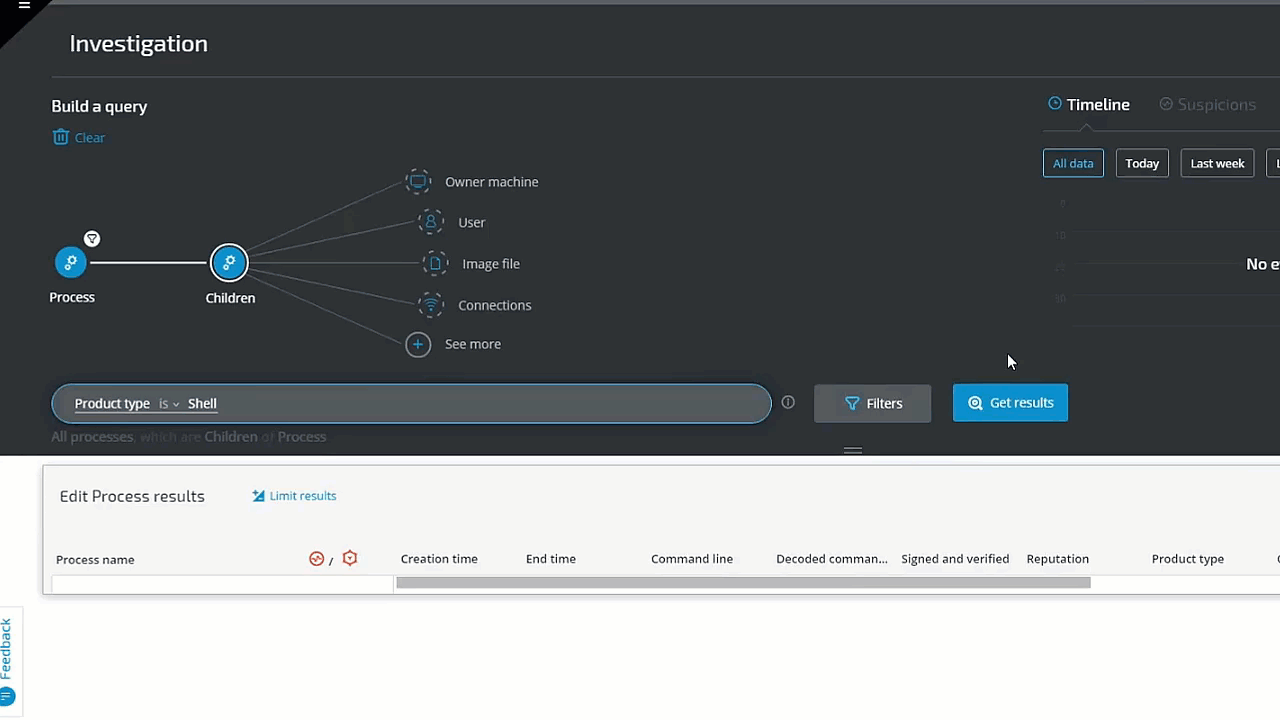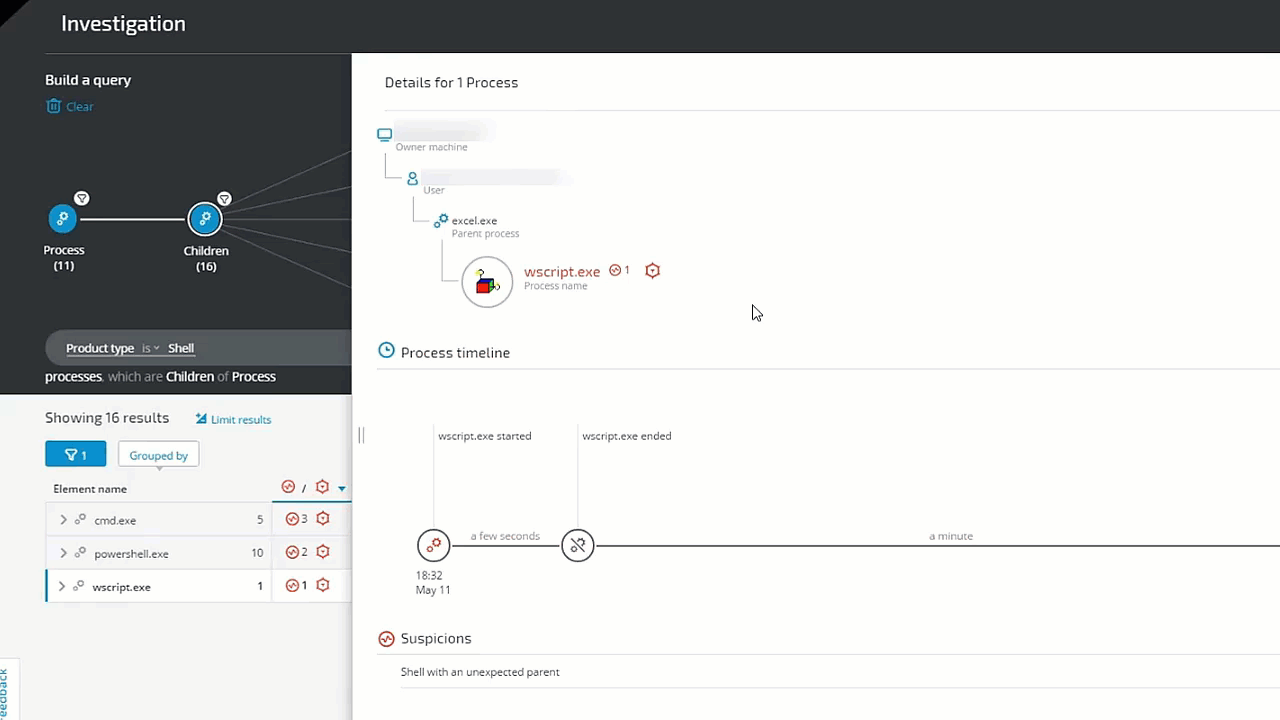
In the following example, we investigate a potential phishing attack. The analyst is hunting for a Microsoft Office or Adobe process whose Type is Shell. The threat hunter simply clicks on Process and selects Product Type 'Adobe' or 'Microsoft', and then adds Children and Product Type 'Shell.' The query results instantly reveal several results for further investigation:
The Cybereason XDR Platform
Another significant capability that contributes to the 10X improvement in threat hunting is the Attack Tree. The Attack Tree is a hunting tool that displays a specific process’s chain of execution from start to finish.
Analysts can use the Attack Tree to:
- Narrow down large data sets to focus on processes with security relevance
- Understand what happened before and after a process was deemed malicious
- Investigate what additional activity occurred in a suspicious execution chain
- Quickly view all properties of every process in an execution chain
- Gain contextual awareness for every process
What are the components of the Attack Tree?
Each process in the Attack Tree is represented by a bubble. In most views of the Attack Tree, processes with the same name are grouped into a single bubble. Each process bubble is connected to its direct relatives (i.e. parent and child processes), with the root process appearing on the far left.
Suspicious processes are outlined in red and appear higher on the screen than other processes with the same parent. Subsequent top-to-bottom ordering is alphabetical by process name.
In the Process Bubble example below, we see:
- The name of process.
- Plus or minus icon to expand or collapse child processes.
- Suspicions icon indicating if the process is connected to one or more suspicions
- Number indicating how many processes are aggregated into that bubble.
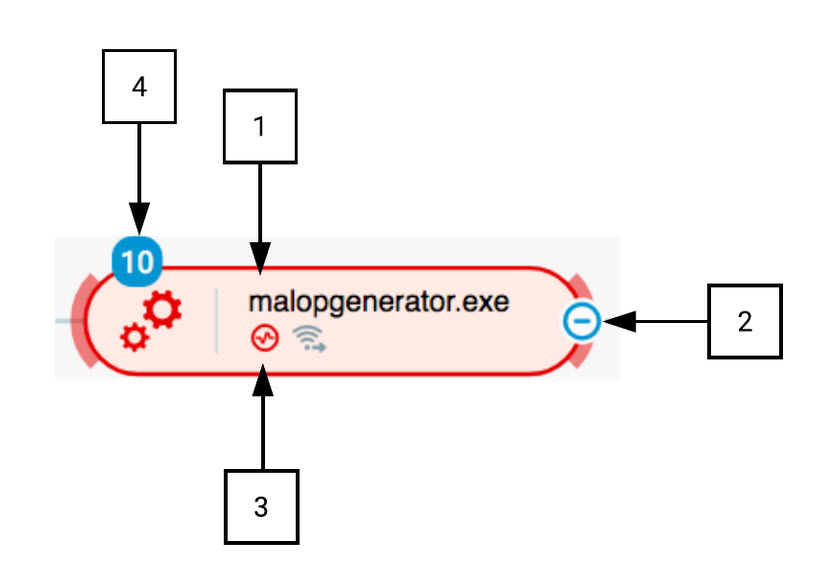
Process Bubble in the Cybereason XDR Platform
The below example depicts the elements and functionality of an Attack Tree. Once you access the attack tree, the process you selected is highlighted and the details of the process are displayed on the right. From here, you have additional viewing options.
From the top right, you can adjust the view of the tree within the UI to center the screen on your process, or to view the tree full screen. You can also adjust what information is actually displayed in the tree from a high-level overview, down to more detailed views.:
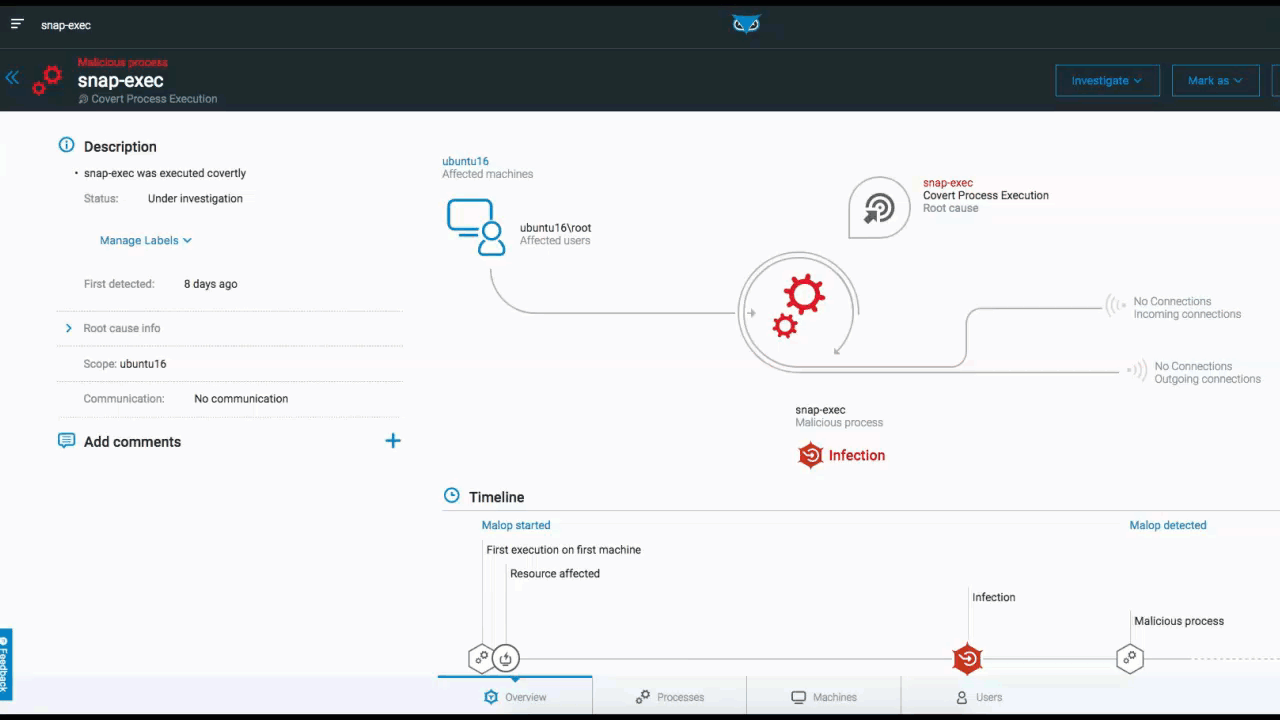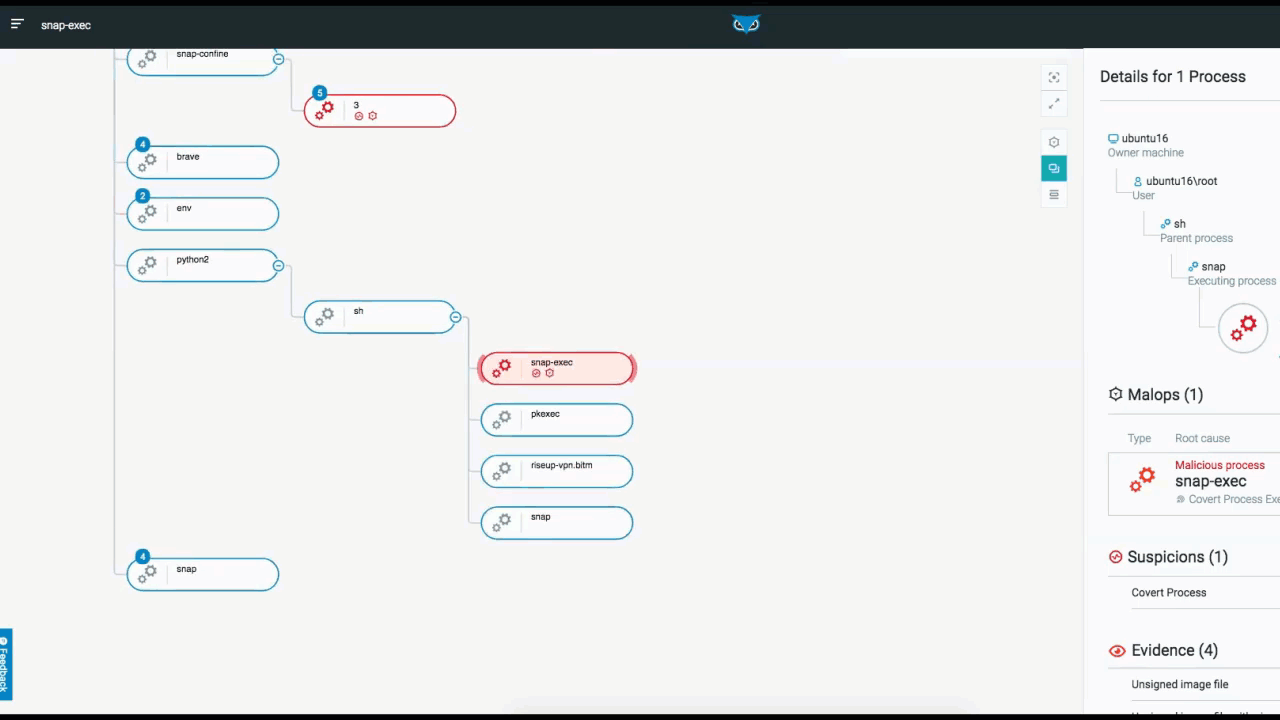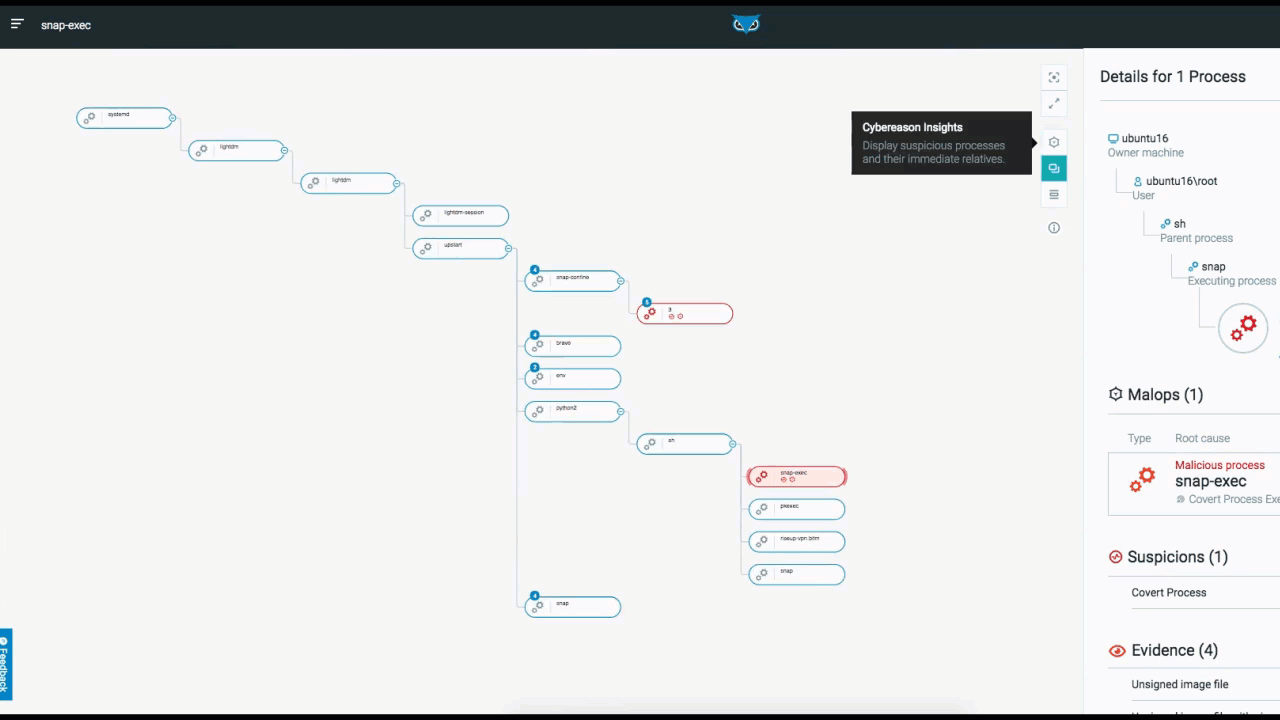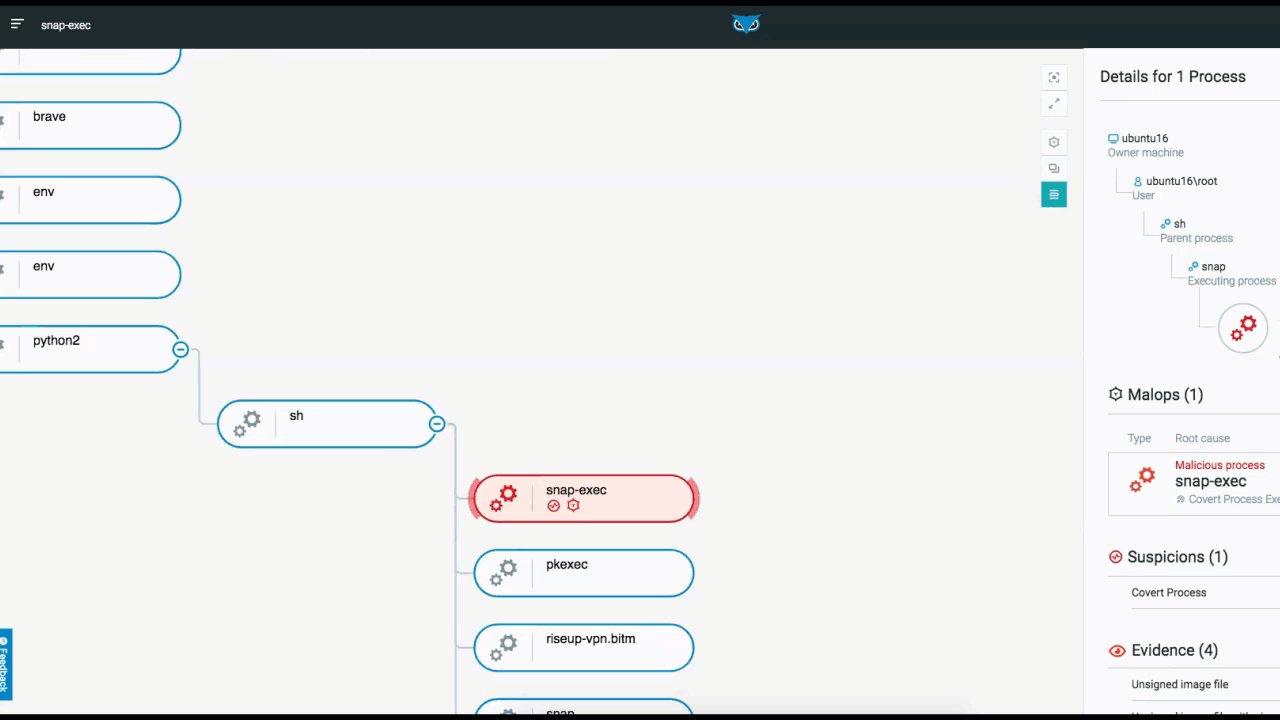
Attack Tree in the Cybereason XDR Platform
In addition to listing processes that are tied to MalOps (malicious operations), Cybereason also notes Suspicions and Evidence (right side of the screen above). Although MalOps require immediate response, there is often additional evidence that is of importance to threat hunters.
SOC teams can now dedicate their Tier 1 analysts to work on the MalOps while their threat hunters can leverage the evidence and other suspicions to develop a hypothesis for their threat hunting campaigns.
Like Malops in general, the attack tree view is Cybereason’s way of displaying the entire story of an attack, a unique feature that enables 10X faster threat hunting compared to manual hunting techniques.
Cybereason is dedicated to teaming with defenders to end attacks on the endpoint, across enterprise, to everywhere the battle is taking place. Learn more about the AI-driven Cybereason XDR Platform or schedule a demo today to learn how your organization can benefit from an operation-centric approach to security.








