Gain insight into the latest attack trends, techniques, and procedures our Incident Response experts are actively facing with the brand new TTP Briefing, a report built on frontline threat intelligence from our global incident response (IR) investigations, enriched by noteworthy detections from our SOC.
The TTP Briefing is grounded in real-world investigations led by Cybereason’s IR and SOC teams across industries and geographies. The findings highlight thorny challenges organizations face, even with baseline protections like EDR and MFA, revealing where attackers are finding success - and where defenders need to focus to harden against, respond to, and recover from today’s most pressing threats.
This first edition of our TTP Briefing covers intel gathered from January through May. Let’s explore a few key findings:
Most Common Threat Types
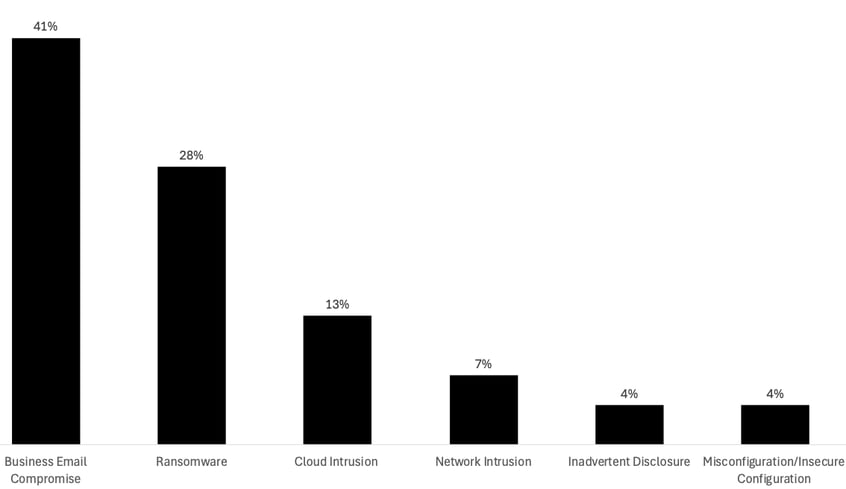
- Business Email Compromise (BEC) was the most common incident type, accounting for 41% of observed threats.
- Ransomware followed closely at 28%, with variants like Qilin, Medusa, and Play showing increased activity.
- Cloud intrusions made up 13% of incidents
Initial Intrusion Vector (How Are They Getting In?)
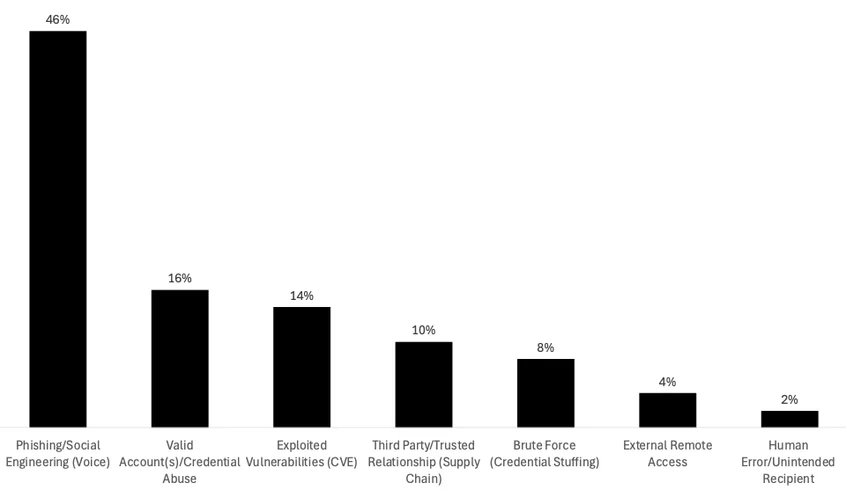
Unsurprisingly, phishing and social engineering remain the dominant intrusion vector (46%), followed by credential abuse and exploited vulnerabilities.
In our report, we’ve combined the various email- and sms-based phishing tactics along with social engineering tactics that may involve stolen credentials and repeated helpdesk calls to trick agents into resetting or temporarily deactivating MFA.
MFA Coverage Still Lacking & MFA Bypass is Widespread
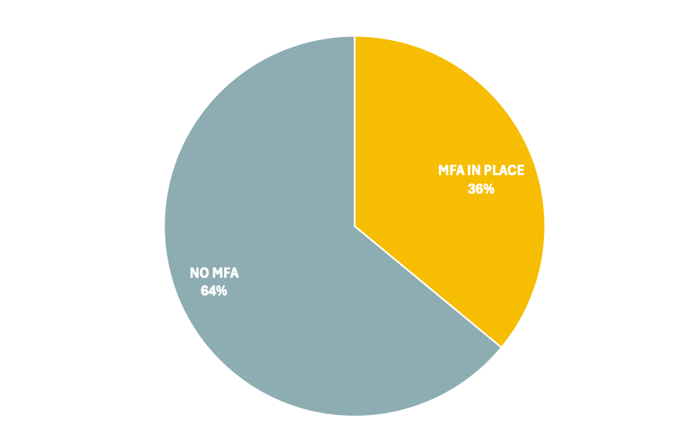
Only 36% of BEC victims had MFA in place at the time of the account compromise, which is a big concern in itself, but among those that had MFA in place, attackers were able to bypass MFA protection in over half of cases.
Most Targeted Industries & Company Sizes
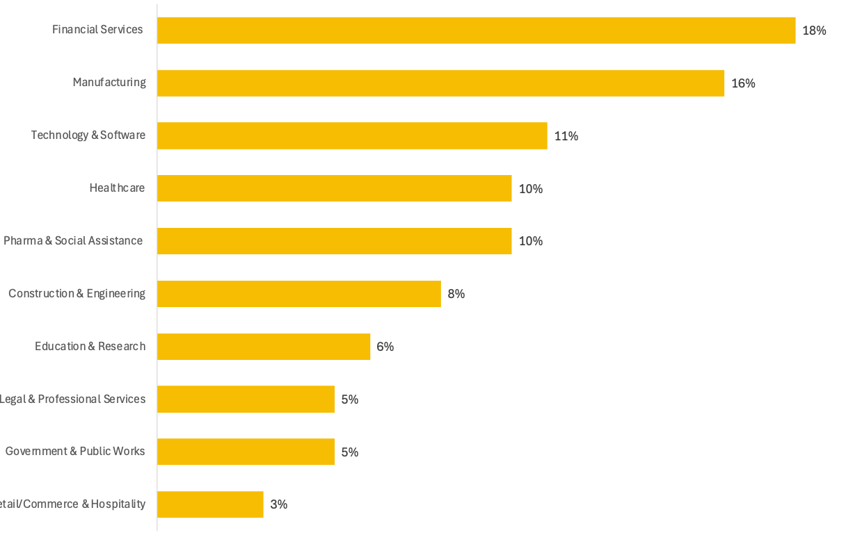
Across all industries, organizations with revenue between $11M and $100M were the most frequently impacted, underscoring the pressure on mid-sized companies to mature their defenses without enterprise-sized resources.
Tactics Across the Intrusion Path
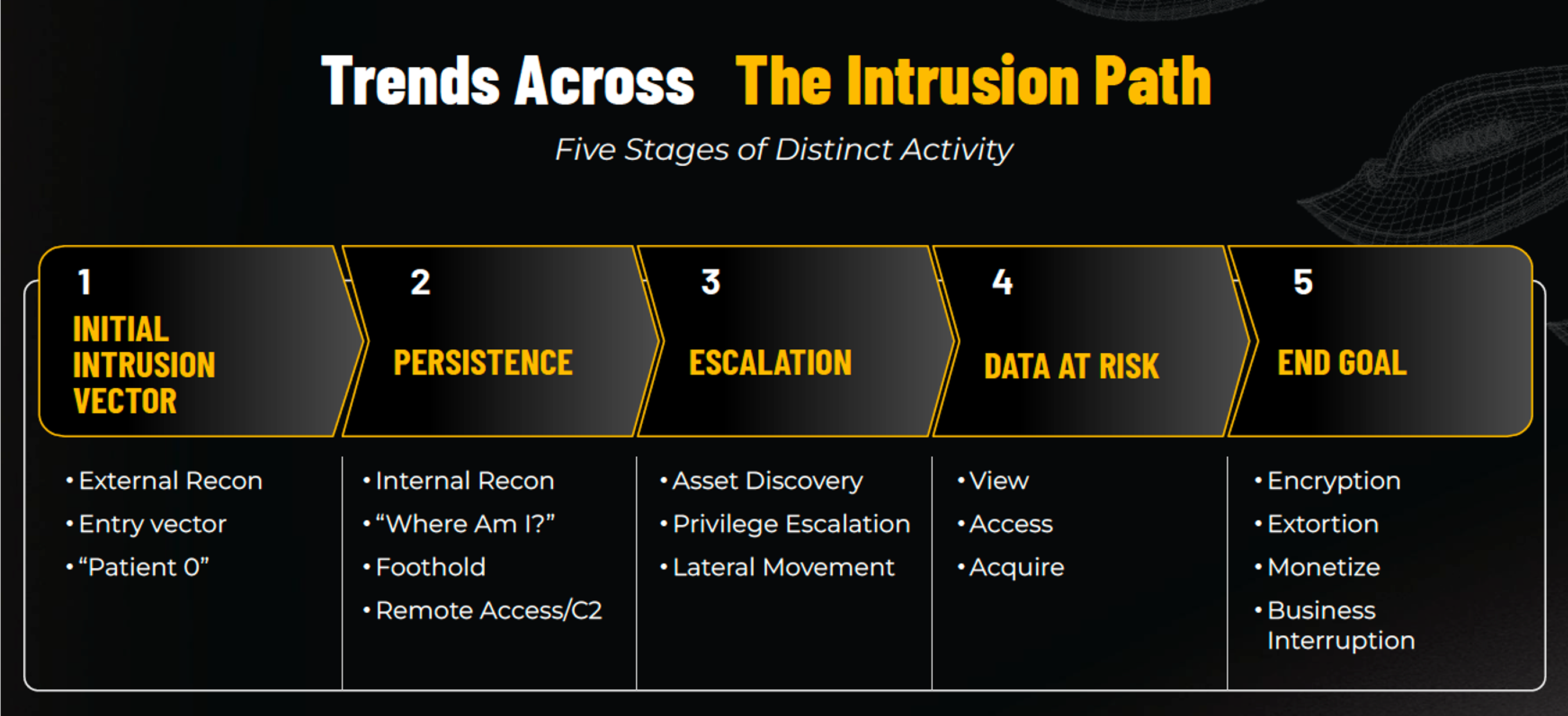
The TTP Briefing provides data across the five stages of the intrusion path, from initial intrusion to persistence and escalation techniques, to exfiltration and monetization tactics. Noteworthy findings include:
- Remote access tools like AnyDesk, MeshAgent, and ScreenConnect were common in establishing persistence.
- Escalation often leveraged Mimikatz and LSASS dump techniques.
- Data exfiltration was achieved primarily using utilities like RClone and WinSCP.
- For nearly 1 in 5 cases (18%), attackers leveraged living-off-the-land binaries (LOLBins) to avoid detection, move laterally, and deploy software including remote access tools and malware.
A Look Into Dwell Time
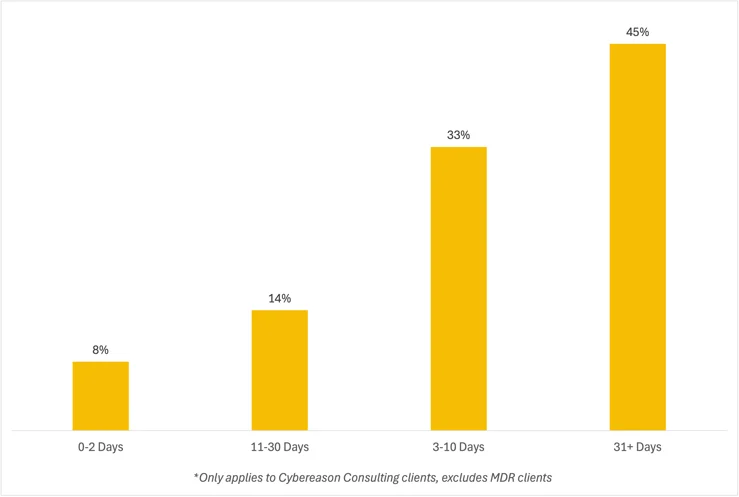
In the TTP Briefing, we excluded any MDR clients and measured dwell time as the initial date of the compromise until our IR team was engaged. We saw dwell time longer than 31 days in 45% of cases, which is very far from ideal.
Often, delays weren’t just due to detection gaps, but also lack of a proper incident response plan and needing to find and onboard vendors to run the investigation. We strongly encourage security and risk leaders to build a Resilience Retainer that matches their needs and can provide a path toward increased preparedness and effective response ahead of a new incident.
If you would like more information about this report, our team is available 24x7 at response@cybereason.com



.png)







