
Copyright Phishing Lures Leading to Rhadamanthys Stealer Now Targeting Europe
Analysis of new Rhadamanthys infostealer campaign in Europe and malware breakdown

Cybereason Team
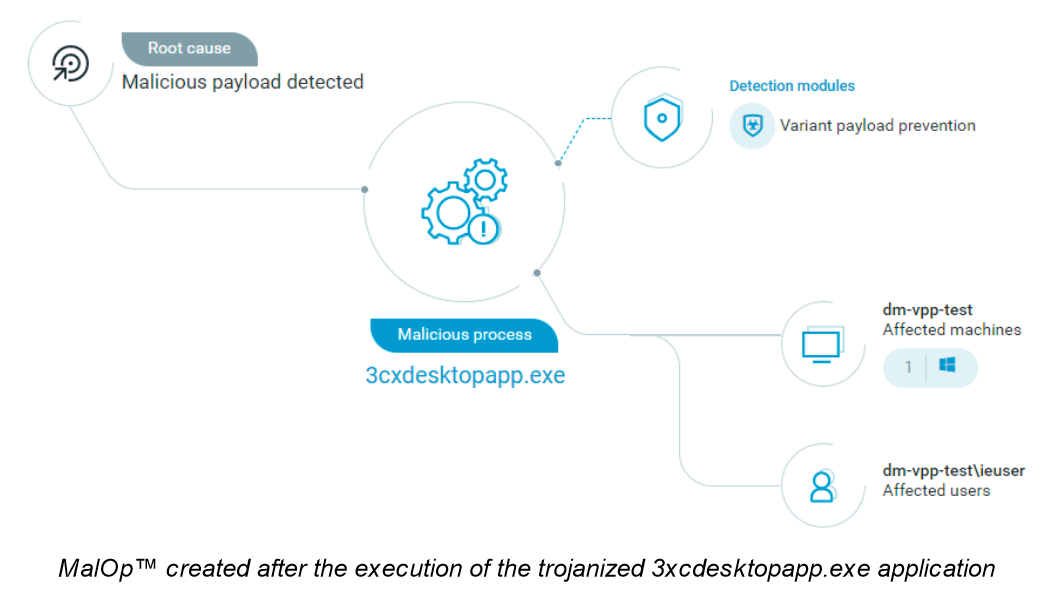
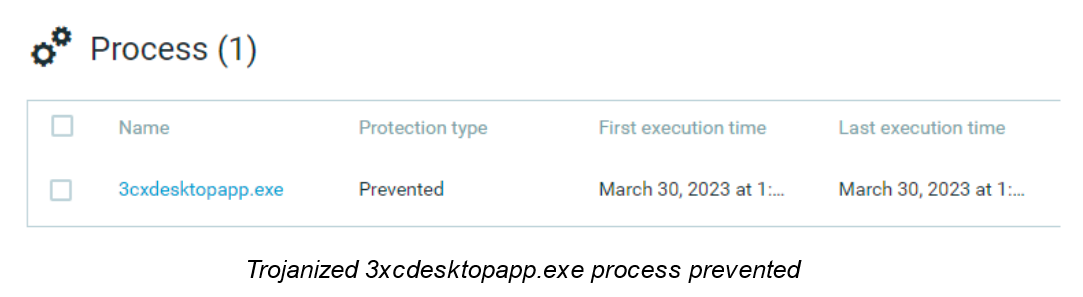
The Cybereason Defense Platform detects and prevents the ongoing 3CXDesktopApp supply chain attack targeting millions of users of the popular 3CX Voice Over Internet Protocol (VOIP) desktop client.
Organizations leveraging Cybereason NGAV are protected from this attack. In addition, Cybereason’s Global Security Operations Center (SOC) team added Indicators of Compromise (IOCs) to the Cybereason Global Threat Intelligence Server to automatically detect the presence of the exploits.
3CXDesktopApp is an application developed by 3CX that allows users to make calls, video conferences, and check voicemails. Threat actors, suspected to be state-sponsored and operating out of North Korea, trojanized this application to add an installer that communicates with various command-and-control (C&C) servers to retrieve a malicious payload.
This ongoing attack puts 12 million Windows and MacOS users at risk of compromise at 600,000 companies across 190 countries.
The trojanized 3CXDesktopApp pulls the icon (ICO) files from Github. These ICO files contain base64 encoded strings that point to the C&C servers hosting the final stage information stealer. The final payload targets web browsers and may lead to sensitive data exposure and exfiltration. This content includes browsing history, cookies, cached data and images, bookmarks, auto-fill forms, and user logins.
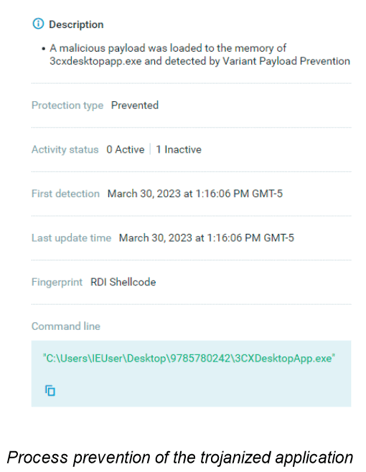
According to Cybereason’s Global SOC Threat Alert, the compromised 3CXDesktopApp is the first stage in the attack chain and uses the DLL side-loading technique to load a rogue DLL (ffmpeg.dll). Ffmpeg.dll loads d3dcompiler_47.dll to its memory and decodes it with the RC4 algorithm, which reveals a shellcode and another binary. The shellcode allocates memory using the VirtualAlloc function and writes the binary, named samcli.dll, into the allocated memory.
Then, the payload tries to access the IconStorages GitHub page to pull an ICO file containing the command-and-control servers. The payload uses this file to communicate with the C&C server and retrieve the final stage of the attack.
The GitHub page used in this attack, raw.githubusercontent[.]com/IconStorages/images/main/, has been taken down as of the time of writing.
According to 3CX, the issue appears to be one of the bundled libraries they compiled into the Windows Electron App via GIT.
Cybereason NGAV includes Variant Payload Protection (VPP), which detects and prevents the shellcode associated with the exploitation of the application from the beginning of this attack.
Cybereason customers should:
Cybereason customers can download the full Threat Alert for further analysis and hunting queries.
A public version of the Threat Alert is available here.
Cybereason NGAV includes Variant Payload Prevention, which performs real-time analysis of memory executions to detect every fracture of malicious code. It also identifies previously unknown malware based on its “genetic” similarities to existing malware, creating a powerful fingerprint immune to subtle code modifications.

Cybereason is dedicated to partnering with Defenders to end attacks at the endpoint, in the cloud and across the entire enterprise ecosystem. Only the AI-driven Cybereason XDR Platform provides predictive prevention, detection and response that is undefeated against modern ransomware and advanced attack techniques. The Cybereason MalOp™ instantly delivers context-rich attack intelligence across every affected device, user and system with unparalleled speed and accuracy. Cybereason turns threat data into actionable decisions at the speed of business.
All Posts by Cybereason Team
Analysis of new Rhadamanthys infostealer campaign in Europe and malware breakdown

In this Threat Analysis Report, Cybereason explores the fake installer, ValleyRAT

Analysis of new Rhadamanthys infostealer campaign in Europe and malware breakdown

In this Threat Analysis Report, Cybereason explores the fake installer, ValleyRAT
Get the latest research, expert insights, and security industry news.
Subscribe